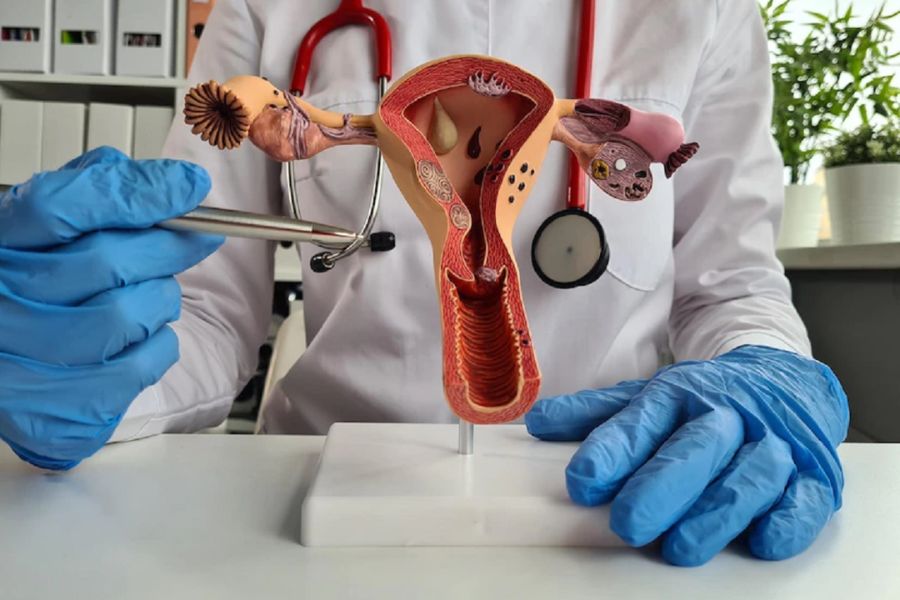
Cervical cancer affects women across all ages and backgrounds; good news is doctors are able to prevent it in most cases. When women understand the types of cervical cancer, recognize early symptoms, and take advantage of screening and vaccination, they significantly reduce their risk.
During Cervical Cancer Awareness Month, we are joining in the global conversation to keep attention on cervical health.
How familiar are you with cervical cancer prevention options?
What Is Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer develops in the cervix, the lower part of the uterus. The disease begins when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably and invade healthy tissue. In nearly all cases, a long-term infection with high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) triggers these cellular changes.
HPV spreads through sexual contact, and most sexually active people encounter it at some point. The body often clears the virus naturally, but when it does not, cervical cancer can develop over time.
Types of Cervical Cancer
Doctors classify cervical cancer based on the type of cells affected.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma starts in the thin, flat cells lining the outer cervix. This form accounts for 70–80% of cervical cancer cases, making it the most common type.
Adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma forms in the glandular cells that produce mucus inside the cervical canal. Although less common, this type has increased in recent years and can be harder to detect through routine screening.
Rare Cervical Cancer Types
Some women develop mixed forms, such as adenosquamous carcinoma. These rare types contain both squamous and glandular cells.
Causes and Risk Factors
Persistent infection with high-risk HPV types, especially HPV-16 and HPV-18, causes most cervical cancers. Several factors increase the likelihood of infection progressing to cancer:
- Early sexual activity or multiple sexual partners
- A weakened immune system, including HIV infection
- Smoking, which damages cervical cells and weakens immune defenses
- Lack of access to regular screening
- No HPV vaccination
Understanding these risk factors helps women take proactive steps to protect their health.
Cervical Cancer Symptoms
Cervical cancer often produces no symptoms in its early stages, which makes routine screening essential. As the disease progresses, women may experience:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding, including after sex or menopause
- Unusual vaginal discharge with a strong odor or blood
- Pelvic pain or pain during intercourse
Women should seek medical advice if they notice any persistent or unusual changes.
DID YOU KNOW?
According to International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Over 340,000 women die from it annually: most in low- and middle-income countries. Early detection and vaccination can prevent up to 90% of cases.
How Women Can Prevent Cervical Cancer
Women can prevent cervical cancer through early action and consistent care.
Get the HPV Vaccine
The HPV vaccine protects against the virus types responsible for most cervical cancers. Health experts recommend vaccination before exposure to HPV, but older teens and adults can still benefit.
Attend Regular Cervical Screenings
Pap tests and HPV tests detect abnormal cell changes before cancer develops. Regular screening saves lives by identifying problems early.
Practice Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Women can lower their risk by avoiding smoking, practicing safer sex, and maintaining regular gynecological checkups.
Global Cervical Cancer Statistics
Cervical cancer remains a significant global health challenge:
- Cervical cancer ranks as the fourth most common cancer in women worldwide
- The disease causes approximately 660,000 new cases and 350,000 deaths each year
- More than 90% of deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries due to limited access to screening and treatment
Countries with strong vaccination and screening programs have dramatically reduced cervical cancer rates.
Cervical cancer does not have to claim lives. Education, vaccination, and screening give women the power to prevent this disease. When women act early and encourage others to do the same, they help move the world closer to eliminating cervical cancer.
Disclaimer: This post is for educational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. Please consult with a healthcare professional for personalized medical guidance and if you have any health concerns.